√100以上 greenhouse gases names with formula 193950
GHG (Total Annual Greenhouse Gas Emissions for All Employees Metric Tons CO 2) = AKGM * TVMT * 0001 Notes about the calculation's components AKGM is calculated as described above TVMT is calculated as described above Multiplying 0001 is used to convert kilograms to metric tons (ie, 1,000 KG)Find the perfect Greenhouse Gases stock photos and editorial news pictures from Getty Images Select from premium Greenhouse Gases of the highest qualityGreenhouse gases are gases—like carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane, and nitrous oxide—that keep the Earth warmer than it would be without them The reason they warm the Earth has to do with the way energy enters and leaves our atmosphere
Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia
Greenhouse gases names with formula
Greenhouse gases names with formula-Nitrous oxide, N 2 O; The AGGI—short for Annual Greenhouse Gas Index—reports the combined warming influence of all longlived greenhouse gases as a fraction of their influence in 1990 Ever since people began grappling with the realization that human activities are changing the climate, scientists and decisionmakers have struggled to come up with simple ways to talk about the




Chlorofluorocarbon Cfc Definition Formulas Examples
greenhouse gas, any gas that has the property of absorbing infrared radiation (net heat energy) emitted from Earth's surface and reradiating it back to Earth's surface, thus contributing to the greenhouse effect Carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapour are the most important greenhouse gases (To a lesser extent, surfacelevel ozone, nitrousGreenhouse Gas (GHG) Reduction As outlined in Executive Order (EO) , Planning for Federal Sustainability in the Next Decade, the goal of reducing greenhouse gas emissions is to minimize the contributions to the greenhouse effect which contributes to global warming and subsequent adverse environmental and human healthGHG reduction is managed by the followingGreenhouse Gas Emissions Calculation Methodology for Article 7a of the Fuel Quality Directive Report to the Directorate General for Climate Action of the European Commission Washington DC The International Council on Clean Transportation (ICCT) ACKNOWLEDGMENTS With thanks to Wojciech Winkler and Lars Mueller (DG Clima);
Methane as a Greenhouse Gas Methane, along with carbon dioxide and other molecules, contributes significantly to the greenhouse effect Reflected energy from the sun in the form of longer 265–298 Fluorinated gases A group of gases that contain fluorine, including hydrofluorocarbons, perfluorocarbons, and sulfur hexafluoride, among other chemicals These gases are emitted from a variety of industrial processes and commercial and household uses and do not occur naturallyGreenhouse gas inventories3 Why do greenhouse gas levels matter?
The greenhouse effect Without greenhouse gases in its atmosphere , the Earth would be about 18°C colder on average than it is now That would make itChlorodifluoromethane or difluoromonochloromethane is a hydrochlorofluorocarbon This colorless gas is better known as HCFC22, or R22, or CHClF 2 It is commonly used as a propellant and refrigerant These applications are being phased out in developed countries due to the compound's ozone depletion potential and high global warming potential, although global use of R22 Each greenhouse gas is subject to different chemical reactions in the atmosphere and to different mechanisms of alteration or removal Thus projections of future concentrations must account not only for emissions but also for transformations in the atmosphere In addition, the various greenhouse gases have different energyabsorbing properties




Parent S Choice Gentle Non Gmo Powder Baby Formula 34 Oz Can Walmart Com
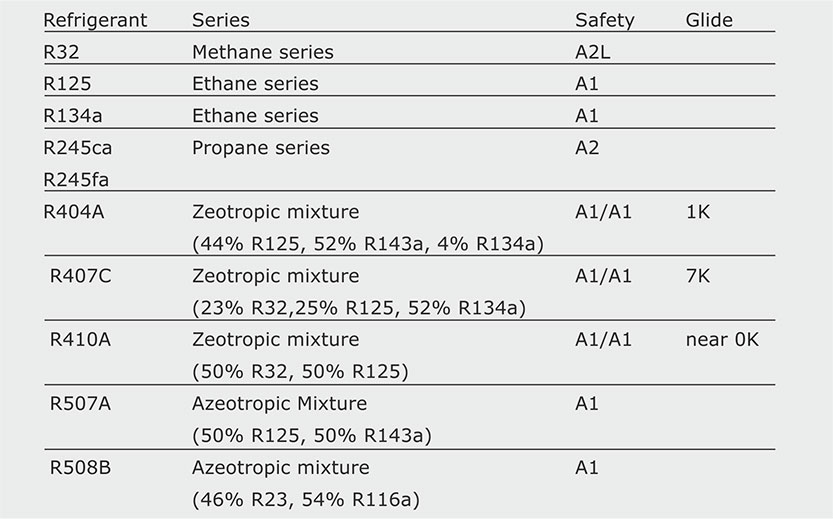



5 4 Refrigerant Types Swep
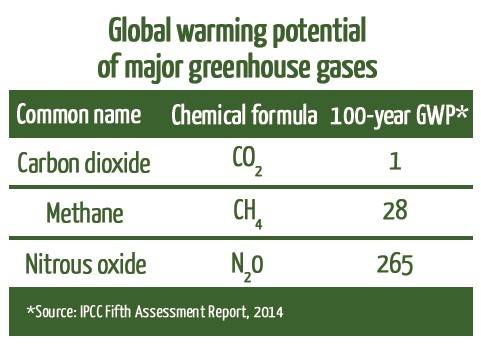
Major greenhouse gases are Carbon dioxide Water Vapour Methane Ozone Nitrous oxide Chlorofluorocarbons The IPCC's Task Force on National Greenhouse Gas Inventories (TFI) develops and refines an internationally agreed methodology and software for the calculation and reporting of national greenhouse gas emissions and removals, and encourages the use of this methodology by countries participating in the IPCC and by Parties to the United Nations Framework ConventionGreenhouse gases have very different warming effects one tonne of methane does not have the same impact on warming as one tonne of CO 2Carbon dioxide equivalents (CO 2 e) attempt to convert the warming impact of the range of greenhouse gases into a single metric This is done by multiplying each gas by its 100year 'global warming potential' value the amount of warming one




Chemmatters April Cow Power




Current Greenhouse Gas Concentrations
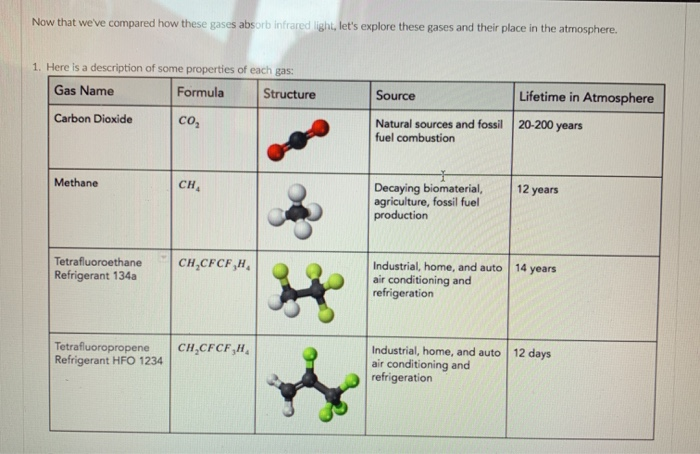
The greenhouse effect happens when certain gases, which are known as greenhouse gases, accumulate in Earth's atmosphereGreenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), ozone (O 3), and fluorinated gases Greenhouse gases allow the sun's light to shine onto Earth's surface, and then the gases, such as ozone,Greenhouse gas Chemical formula Global Warming Potential, 100year time horizon Atmospheric Lifetime (years) Global Warming Potential and Atmospheric Lifetime for Major Greenhouse Gases;Let's consider the principal GHGs one at a time, starting with water vapor, the most abundant greenhouse gas in the atmosphere according to NOAA's National Climatic Data Center (NCDC) Water Vapor Carbon Dioxide (CO 2) Methane (CH 4) Nitrous oxide (N 2 O) Fluorinated Gases (HFCs, PFCs, SF 6) References and Resources




Name Of Variables Symbols And Dimensional Equation Of Input Variables Download Table



How To Calculate Supply Chain Emissions The Right Way
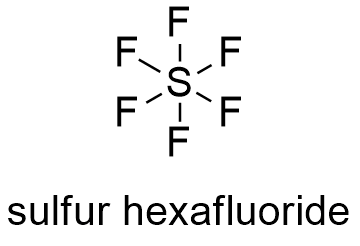
Fluorinated gases Hydrofluorocarbons, perfluorocarbons, sulfur hexafluoride, and nitrogen trifluoride are synthetic, powerful greenhouse gases that are emitted from a variety of industrial processesWhen we talk about greenhouse gases, we're referring to carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, hydrofluorocarbons, perfluorocarbons and sulphur hexafluoride How are greenhouse gases changing the climate?CFCs (chlorofluorocarbons) The greenhouse



4 41 Triple Only Understand How To Write The Structural And Displayed Formulae Of An Ester Given The Name Or Formula Of The Alcohol And Carboxylic Acid From Which It Is Formed And



Sconradscience Weebly Com
Greenhouse gases that occur both naturally and from human activities include water vapor, carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O) and ozone (O 3) Other greenhouse gases have essentially no natural sources, but are side products of industrial processes or manufactured for human purposes such as cleaning agents, refrigerants, and electricalAny gas in the Earth's atmosphere capable of trapping heat is defined as a greenhouse gas Major greenhouse gases include water vapor (H2O), carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), ozone (O3), chlorofluorocarbons (CFC), and others Name of greenhouse gas Recipe Shortcut (formula) Gumdrop model Ozone 3 oxygen atoms O 3 Nitrous oxide 2 nitrogen atoms and 1 oxygen atom N 2 O Carbon dioxide 1 carbon and 2 oxygen atoms CO 2 Water vapor 2 hydrogen atoms and 1 oxygen atom H 2 O Methane 1 carbon atom and 4 hydrogen atoms CH 4



Cityofdubuque Org




Topic 8 2 Thermal Energy Transfer Formative Assessment
Environment Canada (EC) created the Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Emissions and Criteria Air Contaminants (CAC) Calculator to help environmental groups and other users estimate GHG and CAC emission reductions from different environmentally sound actions undertaken during the lifespan of their projects The role of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere has nothing at all to do with their molecular weights What makes a greenhouse gas function in the Carbon dioxide, or CO2, is a greenhouse gas that is emitted by the natural carbon cycle and by human activities, such as burning fossil fuels, notes the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) Normally, CO2 gas emitted into the atmosphere is removed in roughly equal amounts by oceans and plants



Directions Copy Paste Questions And Highlight




No2 Structure Nitrogen Dioxide Formula Structure Chemical Name Properties Uses Of Nitrogen Dioxide
Measuring greenhouse gas emissions The three most important greenhouse gases in the atmosphere are carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), methane (CH 4) and nitrous oxide (N 2 O) While carbon dioxide is the greenhouse gas we hear the most about, methane and nitrous oxide have greater global warming potential ( GWP ) Methane has a GWP of 25 for a 100year Greenhouse gases are certain molecules in the air that have the ability to trap heat in the Earth's atmosphere Some greenhouse gases, like carbon dioxide (CO 2) and methane (CH 4), occur naturally and play an important role in Earth's climateAtmospheric concentrations of several important greenhouse gases have increased significantly since largescale industrialization began around 0 years ago4 Fossil fuel combustion converts carbon that had been stored deep in the Earth to carbon dioxide that enters the atmosphere




Greenhouse Effect And Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Ffectffect Ppt Download



Greenhouse Gas Energy Saving Products
Additional trace gases produced by industrial activity that have greenhouse properties include nitrous oxide (N 2 O) and fluorinated gases (halocarbons) The latter includes sulfur hexafluoride, hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), and perfluorocarbons (PFCs) Methane Ozone Nitrous oxide Chlorofluorocarbons Greenhouse gases are gases that can trap heat They get their name from greenhouses A greenhouse is full of windows that let in sunlight That sunlight creates warmth The big trick of a greenhouse is that it doesn't let that warmth escape Now, over a century later, the mention of greenhouse gas usually evokes thoughts of carbon dioxide (CO 2)That's mainly because changes in the amount of CO 2 in the atmosphere have been linked to the warming of the atmosphere over this past century CO 2 is an important greenhouse gas, and along with water vapor, keeps the Earth warm enough to support life as we




The Dynamic Earth External Radiant Energy From The



Mdpi Com
Carbon Dioxide CO2 1 100* Methane CH4 25 12 Nitrous Oxide N2O 265 121 Chlorofluorocarbon12 (CFC12) CCl2F2 10,0 100 Hydrofluorocarbon23 (HFC23) CHF3 The greenhouse gases that humans do emit directly in significant quantities are Carbon dioxide (CO2) Accounts for around threequarters of the warming impact of current human greenhousegasGiving 1364 4 W m 2 × 07 = 2387 W m 2 e is the emissivity of an object, generally set to 1 for an ideal radiator σ is the StefanBoltzmann constant T is the temperature of the Earth, in Kelvin With accepted values in this equation, the theoretical average temperature of the Earth is 2387 W m 2 = ( 567 × 10 − 8 W m 2 K 4) T 4




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc
/molecular-model-ST002298-579fec515f9b589aa9fe63b9-5b89b2c846e0fb0025646bc0.jpg)



What Is The Name Of The Covalent Compound Ccl4
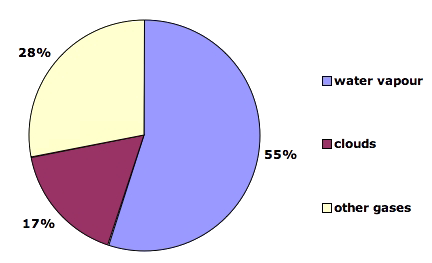
These gases are known as greenhouse gases Below are the most important greenhouse gases that influence Earth's climate system Water vapor (H2O) is the strongest greenhouse gas, and the concentration of this gas is largely2 days ago There are many greenhouse gases but these are some of the most important water vapour, H 2 O;Carbon dioxide, CO 2;




Greenhouse Effect Take Cornell Notes On This Video Nomk Nomk Ppt Download




Chemical Formulas And Symbols Used Download Table
Greenhouse Gases CHAPTER 4 Why some gases are greenhouse gases, but most aren't, and some are stronger than others About Gases The layer model is what is called an idealization of the real world It has the essential ingredient of the greenhouse effect, but it is missing numerous things that are important in the real atmosphere Greenhouse Gases Carbon Dioxide, Water Vapor, Nitrous Oxide, Aerosols Share of Global GHG Emissions 15% A jet airliner leaves condensation trails in the sky Total fan capacity* (cubic feet/minute) = 8 x the greenhouse floor area (square feet) *fan capacity is measured at 010 0125 inches water static pressure Note use a large diameter fan with the smallest motor for the highest efficiency Example 30 foot x 100 foot hoophouse Total fan capacity needed = 8 x 30' x 100' = 24,000 cfm




The Principal Greenhouse Gases And Their Sources Neef




15 Sources Of Greenhouse Gases




Formula 1 S Sustainable Fuel Aims To Save Internal Combustion




Greenhouse Gas An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Global Warming Greenhouse Gas Models For Kids




Global Carbon Cycle An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
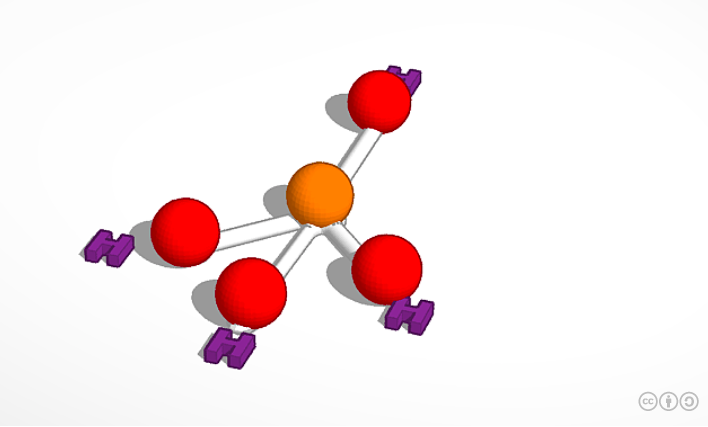



Future Engineers Name That Molecule Challenge Gallery Methane Ch4
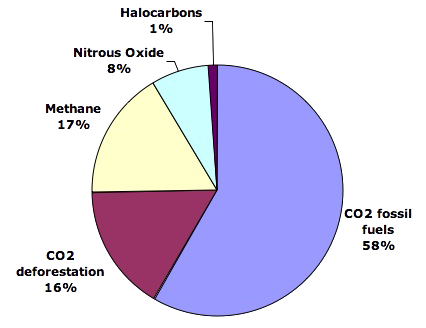



What Gases Are Greenhouse Gases Jean Marc Jancovici




Solved 48 Write The Formula Unit For The Following Chegg Com
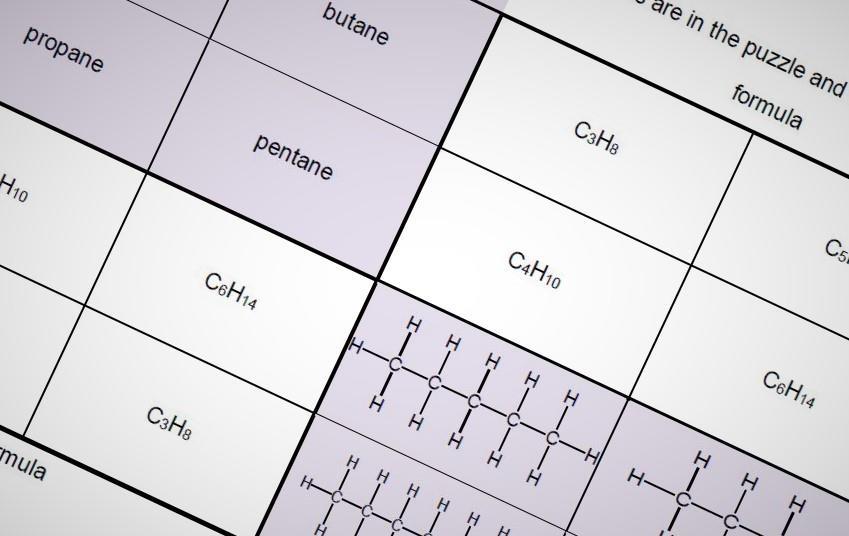



28 Chemistry Puzzles For 14 16 Years Resource Rsc Education



Components Of Air Nitrogen Oxygen Carbon Dioxide Water Vapor And Other Gases
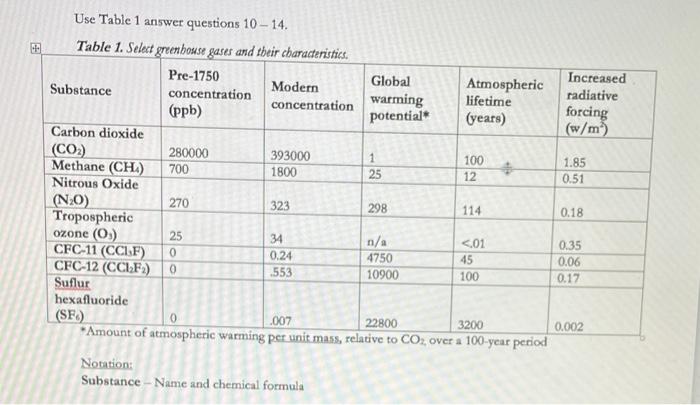



Solved Use Table 1 Answer Questions 10 14 Table 1 Select Chegg Com




Chlorofluorocarbon Cfc Definition Formulas Examples



Methane Gas Source Formula Structure Properties Uses



Atmospheric Greenhouse Gas Concentrations European Environment Agency



Chapter 1 Organic Chemistry Review Hydrocarbons Che 1 Introduction To Organic Chemistry Textbook Libguides At Hostos Community College Library




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia




Carbon Dioxide Molecule High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy




Balanced Chemical Equation Definition Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



Planetary Science
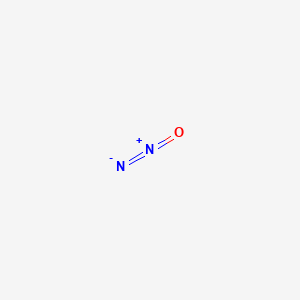



Nitrous Oxide N2o Pubchem



What Gases Are Greenhouse Gases Jean Marc Jancovici




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia



Csiro Publishing International Journal Of Wildland Fire




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Seeg Initiative Estimates Of Brazilian Greenhouse Gas Emissions From 1970 To 15 Scientific Data



Atmo336 Fall 15



1




Solved Give The Name And Symbol Or Formula Of A Group 4a 14 Element Or Compound That Fits Each Description Or Use A Hardest Known Natural Substance B Medicinal Antacid C Atmospheric Gas Implicated




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wikipedia



Usna Edu




Ch 18 Global Climate Change Part 2 Environmental




Difference Between Methane And Fluorinated Gases Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms



What Are The Differences Between Nitrous Oxide And Nitrogen Dioxide Greenhouse Gases Quora



Atmospheric Greenhouse Gas Concentrations European Environment Agency



Hess Com




Questions And Answers Ozone Secretariat



What S The Formula For Laughing Gas Quora




Carbon Dioxide Definition And Examples Biology Online Dictionary




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Evaluation Of The Global Protocol For Community Scale Greenhouse Gas Emission Inventories Gpc Method For Chinese Cities Semantic Scholar




Greenhouse Gases Emissions From Wastewater Treatment Plants Minimization Treatment And Prevention




Bill Gates On How To Invest In Climate Innovation Time
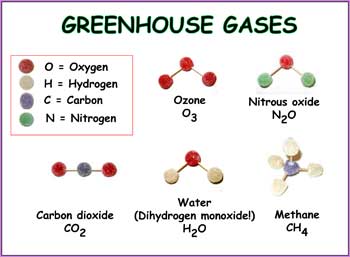



Get Your Gummy Greenhouse Gases Nasa Space Place Nasa Science For Kids




The Hockey Schtick The Greenhouse Equation
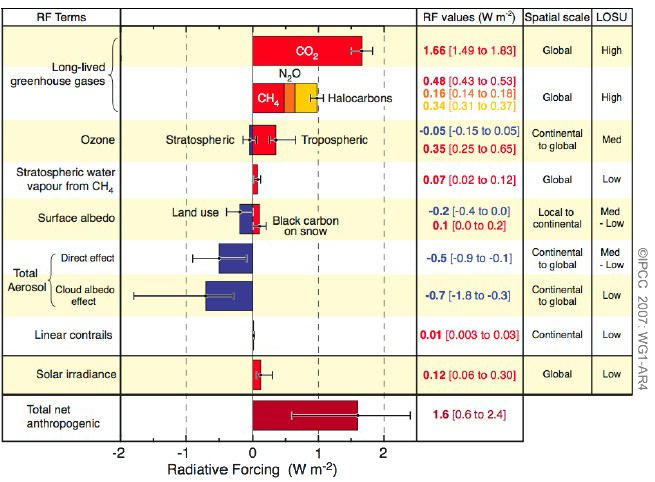



What Gases Are Greenhouse Gases Jean Marc Jancovici




Name Any Two Greenhouse Gases Youtube




Earth S Atmosphere Pdf Troposphere Atmosphere Of Earth




Water Is Also A Greenhouse Gas Lios Soil



Chapter 1 Organic Chemistry Review Hydrocarbons Che 1 Introduction To Organic Chemistry Textbook Libguides At Hostos Community College Library




Boardworks As Chemistry Alkenes Chemistry Intermolecular Force Covalent Bonding



Climate Science Investigations South Florida Energy The Driver Of Climate



Cow Power American Chemical Society



Sulfur Hexafluoride Formula




Ppt Greenhouse Effect Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Global Warming




Which Gases Are Greenhouse Gases American Chemical Society




Arise Curriculum Guide Docest



Methane Ch4 Pubchem



Solved Based On This Information Which Gases Do You Think Chegg Com
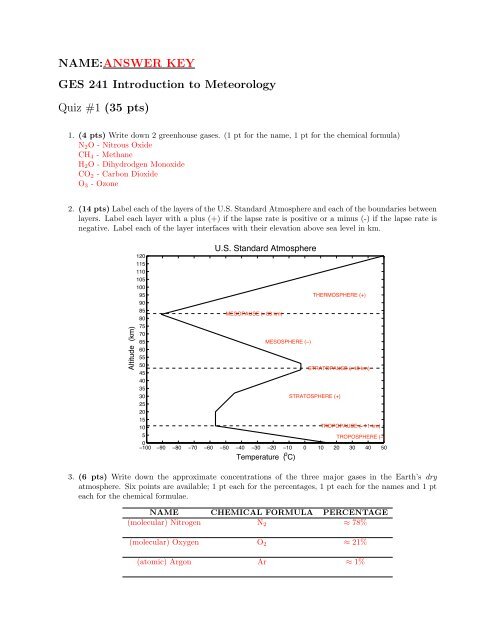



Name Answer Key Ges 241 Introduction To Meteorology Quiz 1




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Hydrocarbon Definition Types Facts Britannica




11 0 Alkane Exam Q S Flashcards Quizlet




Boardworks As Chemistry Alkanes Chemistry Covalent Bonding Structural Formula
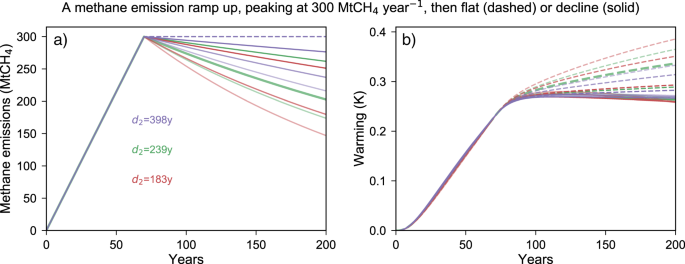



Improved Calculation Of Warming Equivalent Emissions For Short Lived Climate Pollutants Npj Climate And Atmospheric Science
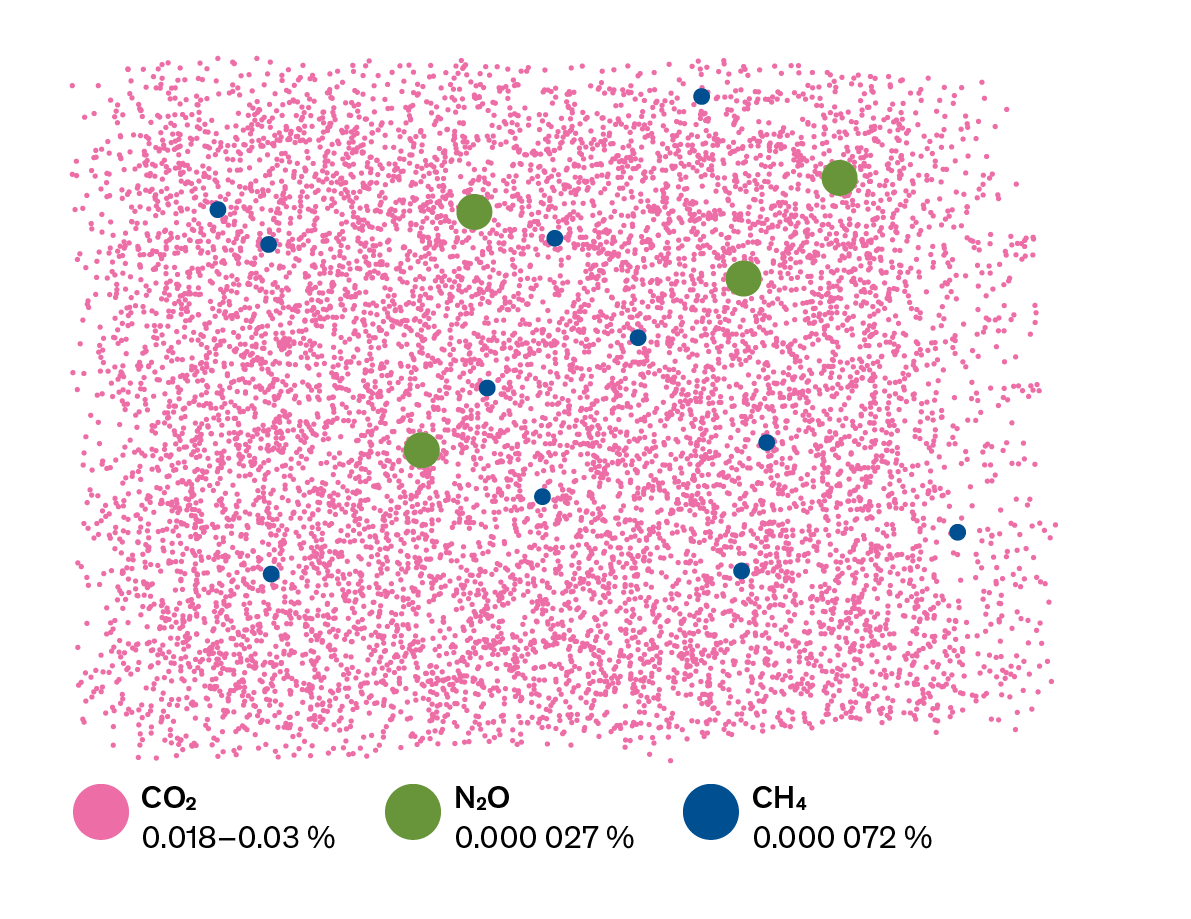



What Are Greenhouse Gases Myclimate




Product Carbon Footprint



Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia
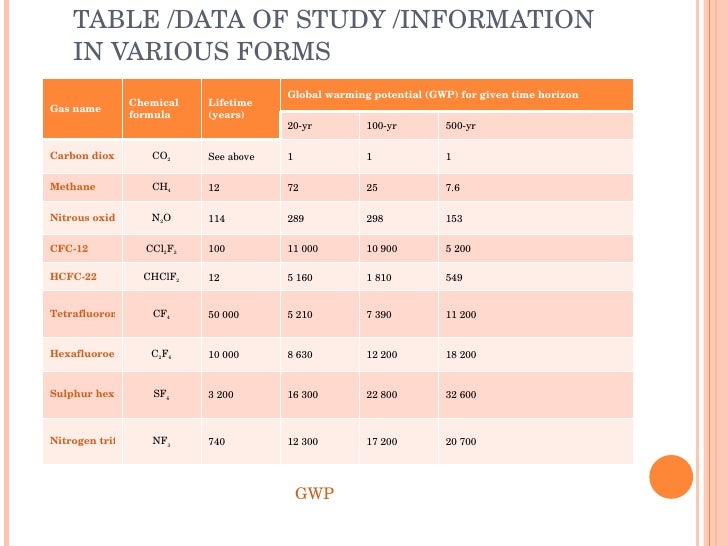



Green House Effect




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Greenhouse Gases Are Rapidly Changing The Atmosphere Climate Central




Pdf Investigation Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions From The Production Of Tin Cans An Evaluation Of The Ecoproit Method Semantic Scholar




Cge Training Materials National Greenhouse Gas Inventories Quality



Ch105 Chapter 7 Alkanes And Halogenated Hydrocarbons Chemistry



Kirkland Signature Procare Non Gmo Infant Formula 42 Oz 4 Pack Costco




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Methane Definition Properties Uses Facts Britannica



1




Explainer Co2 And Other Greenhouse Gases Science News For Students




Gwp Values For Various Ghgs Download Table



1
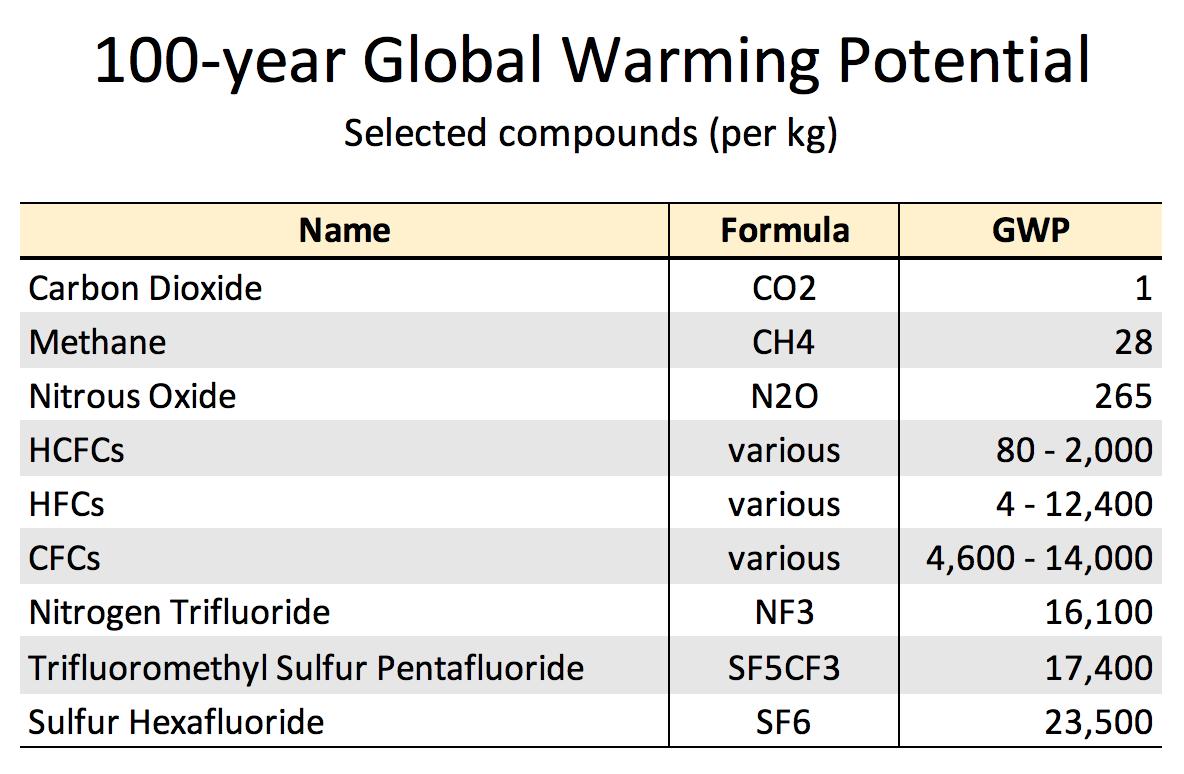



Dr Robert Rohde 5 By Why Do We Care About Sf Well Sf Is The Strongest Greenhouse Gas Ever Evaluated By The Ipcc Per Kilogram It Is 23 500 Times As




How To Calculate Greenhouse Gas Emissions
コメント
コメントを投稿